Electrochemical immunosensors for 2,4-dichlorophenoxyacetic acid based on 3-aminopropyltrimethoxysilane modified electrodes
Published 26-01-2024
Keywords
- Electrochemical Immunosensor,
- 3-aminopropyltrimethoxysilane,
- 2,4-Dichlorophenoxyacetic acid
Copyright (c) 2024 Cambridge Science Advance

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License.
How to Cite
Abstract
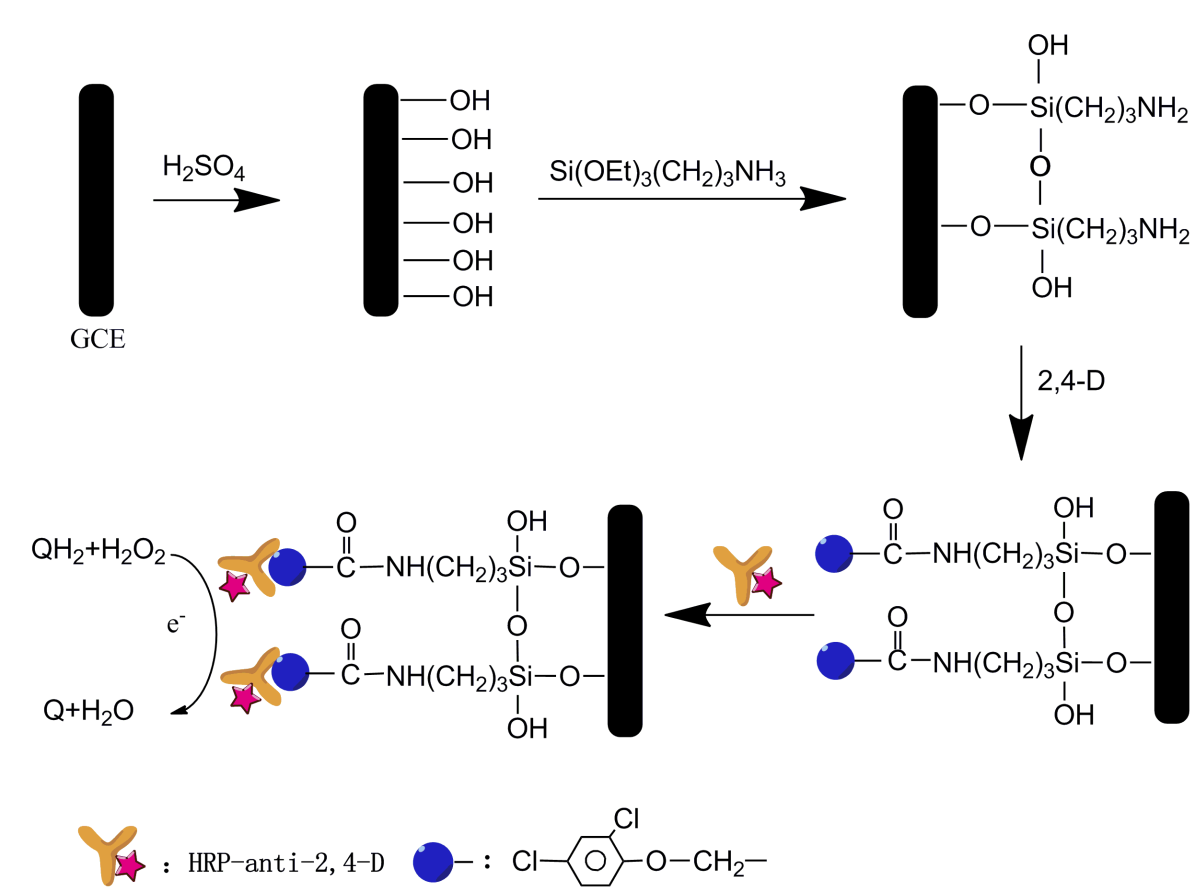
A novel electrochemical immunosensor prepared by direct coating of small molecular hapten on glassy carbon electrode (GCE) is reported for the detection of 2,4-dichlorophenoxyacetic acid (2,4-D). The glassy carbon electrodes were activated by electrochemical method and then were further treated with 3-aminoprpyltriethoxysilane (APS) to functionalize the GCE surface with amino groups for covalent linkage to small molecular hapten of 2,4-D with carboxyl groups. The electrodes were characterized by X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS). The principle of this immunoassay is based on an indirect competitive immunoassay. Analytes of 2,4-D and hapten of 2,4-D immobilized on glassy carbon electrode (GCE) compete for 2,4-D antibodies labeled by horseradish peroxidase (HRP-anti-2,4-D). After complete immunoreaction, the GCE attached HRP-anti-2,4-D tracers was transferred to a substrate solution containing hydroquinone (QH2) and hydrogen peroxide for square wave voltammetry (SWV) detection. Determination conditions were optimized. The SWV anodic peak current decreased linearly with the increase of 2,4-D concentration over the range from 0.10 to 15.0 mg/L 2,4-D with a detection limit of 0.01mg/L. The performance of this electrochemical immunoassay was successfully evaluated with river water spiked with 2,4-D, indicating that this convenient, rapid, and sensitive technique offers great prospect for the monitoring of trace 2,4-D in environment.
References
- C. J. Burns, G. M. H. Swaen, Review of 2,4-dichlorophenoxyacetic acid (2,4-D) epidemiology and toxicology, Crit. Rev. Toxicol. 42 (2012) 768-786.
- World Health Organization, Guidelines for Drinking-Water Quality, third edition, 2006.
- D. L. Hughes , D. J. Ritter, R. D. Wilson , Determination of 2,4-dichlorophenoxyacetic acid (2,4-D) in human urine with mass selective detection, J. Environ. Sci. Health B 36 (2001) 755-764.
- O.P. A. Jr, N. M. Brito, T. C. R. Santos, G. S. Nunes, M. L. Ribeiro, Determination of 2,4-dichlorophenoxyacetic acid and its major transformation product in soil samples by liquid chromatographic analysis, Talanta 60 (2003) 115-121.
- C. Legido-Quigley, J. Oxelbark, E. D. Lorenzi, A. Zurutuza-Elorza, P.A.G. Cormack, Chromatographic characterisation, under highly aqueous conditions, of a molecularly imprinted polymer binding the herbicide 2,4-dichlorophenoxyacetic acid, Anal. Chim. Acta 591 (2007) 22-28.
- M. D. Beeson, W. J. Driskell, D. B. Barr, Isotope dilution high-performance liquid chromatography/tandem mass spectrometry method for quantifying urinary metabolites of atrazine, malathion, and 2,4-dichlorophenoxyacetic acid, Anal. Chem. 71 (1999) 3526-30.
- I. Navrátilová, P. Skládal, The immunosensors for measurement of 2,4-dichlorophenoxyacetic acid based on electrochemical impedance spectroscopy, Bioelectrochemistry 62 (2004) 11-18.
- K. V. Gobi, S. J. Kim, H. Tanaka, Y. Shoyama, N. Miura, Novel surface plasmon resonance (SPR) immunosensor based on monomolecular layer of physically-adsorbed ovalbumin conjugate for detection of 2,4-dichlorophenoxyacetic acid and atomic force microscopy study, Sens. Actuators B 123 (2007) 583-593.
- S. J. Kim, K. V. Gobi, H. Tanaka, Y. Shoyama, N. Miura, A simple and versatile self-assembled monolayer based surface plasmon resonance immunosensor for highly sensitive detection of 2,4-D from natural water resources, Sens. Actuators B 130 (2008) 281-289.
- J. Halámek, M. Hepel, P. Skládal, Investigation of highly sensitive piezoelectric immunosensors for 2,4-dichlorophenoxyacetic acid, Biosens. Bioelectron. 16 (2001) 253-260.
- J. H. Ding, Z. Lu, R. Z. Wang, G.L. Shen, L.T. Xiao, Piezoelectric immunosensor with gold nanoparticles enhanced competitive immunoreaction technique for 2,4-dichlorophenoxyacetic acid quantification, Sens. Actuators B 193 (2014) 568-573.
- M. M. Vdovenko, A. S. Stepanova, S. A. Eremin, N. V. Cuong, N. A. Uskova, I. Y. Sakharov, Quantification of 2,4-dichlorophenoxyacetic acid in oranges and mandarins by chemiluminescent ELISA. Food Chem. 141 (2013) 865-868.
- M. Dequaire, C. Degrand, B. Limoges, An immunomagnetic electrochemical sensor based on a perfluorosulfonate-coated screen-printed electrode for the determination of 2,4-dichlorophenoxyacetic acid, Anal. Chem. 71 (1999) 2571-2577.
- T. Kaláb, P. Skládal, Disposable multichannel immunosensors for 2,4-dichlorophenoxyacetic acid using acetylcholinesterase as an enzyme label, Electroanalysis 9 (1997) 293-297.
- B. B. Dtantiev, A. V. Zherdev, Electrochemical immunosensors for determination of the pesticides 2,4-dichlorophenoxyatietic and 2,4,5-trichlorophenoxyacetic acids, Biosens. Bioelectron. 11 (1996) 179-185.
- H.-S. Byun, D.-S. Yang, S.-H. Cho, Synthesis and characterization of high selective molecularly imprinted polymers for bisphenol A and 2,4-dichlorophenoxyacetic acid by using supercritical fluid technology, Polymer 54 (2013) 589-595.
- W. J. Yang, F. P. Jiao, L. Zhou, X. Q. Chen, X.Y. Jiang, Molecularly imprinted polymers coated on multi-walled carbon nanotubes through a simple indirect method for the determination of 2,4-dichlorophenoxyacetic acid in environmental water. Appl. Surf. Sci. 284 (2013) 692-699.
- M. A. Rahman, M.-S. Won, P.-H. Wei, Y.-B. Shim, Electrochemical detection of ClO3-, BrO3-, and IO3- at a phosphomolybdic acid linked 3-aminopropyl-trimethoxysilane modified electrode, Electroanalysis 18 (2006) 993- 1000.
- Y. H. Yang, M. H. Yang, H. Wang, J. H. Jiang, G. L. Shen, R. Q. Yu. An amperometric horseradish peroxidase inhibition biosensor based on a cysteamine self-assembled monolayer for the determination of sulfides, Sens. Actuators B 102 (2004) 162-168.
- H.J. Shi, G.H. Zhao, M.C. Liu, Z.L. Zhu, A novel photoelectrochemical sensor based on molecularly imprinted polymer modified TiO2 nanotubes and its highly selective detection of 2,4-dichlorophenoxyacetic acid, Electrochem. Commun. 13 (2011) 1404–1407.
- N. Maleki, A. Safavi, H.R. Shahbaazi, Electrochemical determination of 2,4-D at a mercury electrode, Anal. Chim. Acta 530 (2005) 69–74.
- A.-P. Deng, H. Yang, A multichannel electrochemical detector coupled with an ELISA microtiter plate for the immunoassay of 2,4-dichlorophenoxyacetic acid, Sens. Actuators B 124 (2007) 202–208.
