The Influence of Polygonatum King ilium on the Activity of Calcium-Regulating Enzymes and Calcium Ion Concentration in SH-SY5Y Cells Damaged by Aβ25-35 In Vitro
Published 02-07-2024
Keywords
- Alzheimer's disease,
- Polygonatum King ilium and Earthworm Formula,
- SH-SY5Y cells,
- Aβ25-35, calcium ions,
- calcium ion-regulating enzymes
Copyright (c) 2024 Cambridge Science Advance

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License.
How to Cite
Abstract
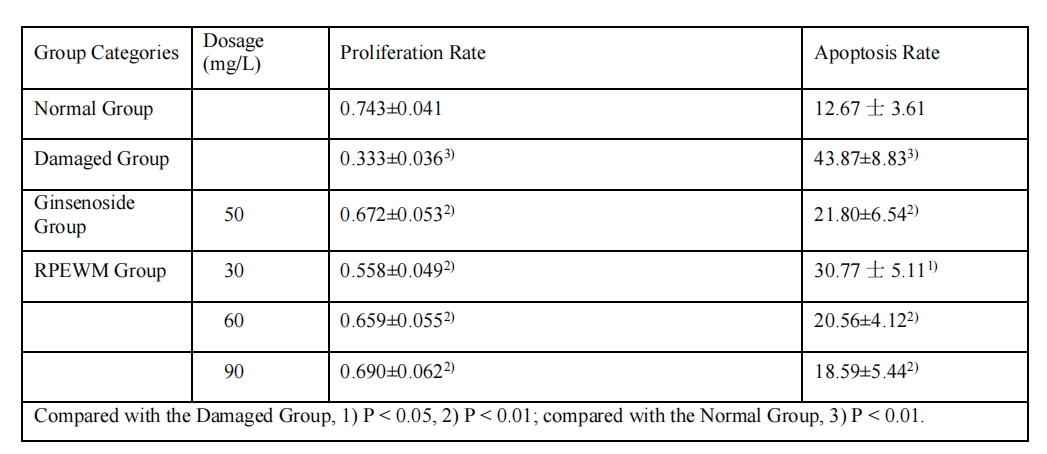
Objective To explore the effects of Polygonatum King ilium and Earthworm Formula (RPEWM) on the activity of calcium-regulating enzymes and free calcium ion (Ca2+) concentration in SH-SY5Y cells with Aβ damage in vitro. Methods SH-SY5Y cells were induced to differentiate with retinoic acid, then damaged by Aβ to mimic Alzheimer's disease (AD) injury. RPEWM extract was added during the AD injury to protect the cells, and its effects on cell proliferation, apoptosis, and the activity of cellular Ca2+-ATPase、Ca2+-Mg2+- ATPase ,as well as free calcium ion concentration were observed. Results RPEWM extract significantly protected cells from AD injury, resisted apoptosis, and promoted cell proliferation; it increased the activity of intracellular Ca2+-ATPase、Ca2+-Mg2+- ATPase, reduced Ca2+ concentration, and showed a dose-dependent relationship. Conclusion RPEWM has a good protective effect on differentiated SH-SY5Y cells with Aβ25-35damage and has a certain therapeutic effect on AD.
References
- Xiao Yi sheng, Zeng Yuan feng, Xu Yue Jing, et al. Research on the anti-Alzheimer's effect of Polygonatum King ilium and Earthworm Formula in mice [J]. Chinese Journal of Clinical Pharmacology and Therapeutics, 2013. 29(2): 152-154.
- Xiao Yi sheng, Cao Yuan feng + Ouyang Hougen, et al. The influence of Polygonatum King ilium and Earthworm Formula on the behavioral cognition and cholinergic system in the brain of aged rats with dementia [J]. Chinese Journal of Clinical Pharmacology and Therapeutics, 2013. 29(4): 146-148.
- Xiao Yi sheng, Zeng Yuan feng, Hou Ji Hua, et al. Research on the protective effect of Polygonatum King ilium and Earthworm Formula on Aβ25-35 damaged differentiated SH-SY5Y cells in vitro [J]. Modern Journal of Integrated Traditional Chinese Medicine and Western Medicine, 2016. 25(20): 2167-2169.
- Xiao Yi sheng, Hou Ji Hua, Wu Qing Hua, et al. Research on the protective effect of Earthworm on focal cerebral ischemic injury in rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Clinical Pharmacology and Therapeutics, 2009. 25(6): 62-64.
- Li Qing, Xiao Yi sheng, Hou Ji Hua, et al. Research on the anti-apoptotic effect of Earthworm in rats with focal cerebral ischemia [J]. Journal of Jiangxi University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2010, 22(2): 63-66.
- Guo Chun Yan, Luo Qiang, Sun Li, et al. Protective effect of Paeonol on H2O2-induced SH-SY5Y neuronal damage [J]. Chinese Traditional Patent Medicine. 2013. 4(20): 2864-2871.
- Joanna A, Ronald E, Eva B, et al. Phenotypic characterization of retinoic acid differentiated SH-SY5Y cells by transcriptional profiling[J]. PloS One,2013.8(5):1-17.
- Hasegawa T, Matsuzaki M, Takeda A, et al. Accelerated alpha-synuclein-aggregation after differentiation of SH-SY5Y neuroblastoma cells[J]. Brain Res,2004.1013(1):51-59.
- Tong Haixia, Zhang Ji Hong. Lu Chunwei, et al. Experimental study on the differentiation of neuroblastoma cells induced by all-trans retinoic acid in vitro [J]. Chinese Medical Engineering, 2007, 15(1): 37-42.
- Christian B. The search for novel avenues for the therapy and prevention of Alzheimer's disease[J]. Drug News & Perspect.2006,19(1):5.
- Kang DE, Roh SE, Eoo JA.et al. The Interface between cytoskeletal aberrations and mitochondrial dysfunction in Alzheimer's disease and related disorders[J]. Experimental Neurobiology,2011.20(2):67-80.
- Du J, Song J. Shi ZR. Research progress of palliative care for patients with advanced Alzheimer's disease[J]. Journal of nursing,2013,8(25):38-41.
- Guo Q. Guo E. Zhong ZG. Research progress in the pathogenesis and treatment of Chinese and Western medicine in the treatment of Alzheimer's disease[J]. Asia Pacific Traditional Medcine,2015,7(6):41-44.
- Mc Geer PL, Rogers J, Mc Geer EG. Inflammation, anti-inflammatory agents, and Alzheimer’s disease: the last 22 years[J]. J Alzheimer’s Dis,2016,54(3):853-857.
- Kim JH. Wang Q. Choi JM, et al. Protective role of caffeic acid in an Aβ25-35-induced Alzheimer's disease model[J]. Nutrition Res Pract,2015,9(5);480-488.
- Clapham DE. Calcium signaling[J]. Cell .2007,131(6):1047-1058.
- Berrocal M, Marcos D, Sepulveda MR, et al. Altered Ca²⁺ dependence of synaptosome plasma membrane Ca²⁺-ATPase in human brain affected by Alzheimer's disease[J]. FASEB ,2009,23(6):1826-1834.
- Guo Q, Sopher BL, Furukawa K, et al. Alzheimer's presenilin mutation sensitizes neural cells to apoptosis induced by trophic factor withdrawal and amyloid beta-peptide: involvement of calcium and oxyradicals[J]. J Neurosci,1997,17(11):4212-4222
- Mattson MP. Calcium and neurodegeneration[J]. Aging Cell.2007.6(3):337-350.
- Zhang S, Chen Y, Wu X, et al. The pivotal role of Ca²⁺ homeostasis in PBDE-47-induced neuronal apoptosis[J]. Mol Neurobiol,2015,38(10):713-721.
