Published 02-07-2024
Keywords
- sports intervention,
- mental health,
- physical contact sports games,
- auditory language disable adolescents
Copyright (c) 2024 The Young Thinker's Review

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License.
How to Cite
Abstract
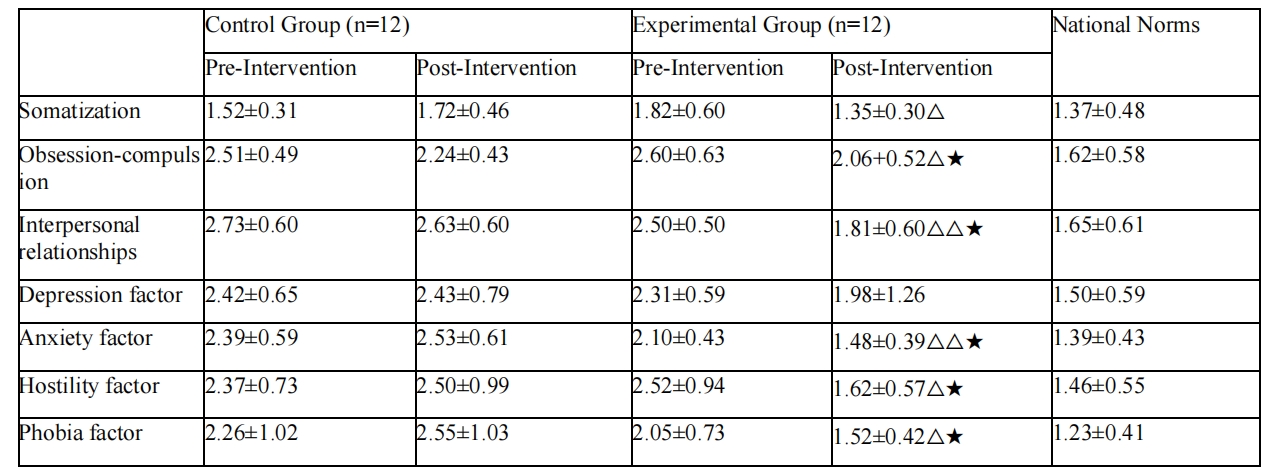
In order to investigate the effects of “body contact” the sports game intervention to improve the mental health of young auditory language disable ,in this experiment ,the auditory language disable students were randomly divided into 24levels of mental health which will be screened low into control group and experimental group ,and the experimental group in the 10 week of the “body contact” the sports game teaching intervention .The results showed that physical contact games played an important role in improving the mental health of auditory language disable adolescents, but there was still some difference between them and the national norm. Specifically, the scores of hostility, compulsion, symptoms, somatization and terror all decreased obviously, and the symptoms of paranoia, interpersonal relationship, anxiety and psychotic symptoms improved, but the effect on depressive factors was not significant.
References
- Naoya Narita, Junko Shimonaka, and Koji Nakazato. "Investigation of the Sense of Efficacy Scale: Exploring the Possibility of Lifelong Developmental Use" [J]. Research in Educational Psychology, 1995 (43): 306-314.
- Johannes Fellinger. Mental health and quality of life in deaf pupils[J]. Eur Child Adolesc Psychiatry,2008(7): 414~423.
- Ray D, BrattonS, Rhine T, Jones L. The effectiveness of play therapy: Responding to the critics[J]. International Journal of Play Therapy, 2001(1):85~108.
- Mei, X. Y., & Chen, F. F. (2011). The impact of physical education intervention through sports games on the psychological health of middle school students. Sports, (18), 76-77.
- Zhao, H. P. (2004). An experimental study on the psychological health effects of physical education teaching methods on junior high school students. Journal of Shenyang Sport Institute, (6), 763-765.
- Gong, G. C., & Sun, N. (2005). The impact of game-like physical activities on the psychological health of primary school students. Physical Education and Research, 20(S1), 135-137.
- Duan, L. H. (2014). An experimental study on the impact of language-based sports games on the physical and mental health and language intelligence of young primary school students. Shanghai: Shanghai University of Sport.
- Wei, S. R. (2013). A brief analysis of the impact of physical games on the physical and mental development of young children. Success (Education Edition), (9), 256-257.
- Xu, G. X. (2007). A collection of psychological case studies on children's game therapy. Jilin: Jilin Publishing Group Co., Ltd.
- Yang, G. X. (2011). Psychological therapy for children with special needs. Beijing: Peking University Press.
- Yang, K. F. (2000). A brief discussion on the psychological quality and related issues of deaf-mute students. Journal of Yuxi Normal College, (2), 9-10.
- Zhang, J. (2008). A report on the psychological health survey of deaf-mute junior high school students in Tianjin. Social Psychological Science, (95), 76-82.
- Lin, Y. P. (2000). A preliminary survey on the psychological health status of deaf-mute students. Chinese Journal of Special Education, (4), 9-12.
- Wang, J. J. (2012). An experimental study on the impact of "physical contact" sports games on the psychological health of primary school students. Zhejiang: Zhejiang Normal University.
- Tang, Z. Y., & Ma, Y. (2001). Research on strengthening physical education and exercise for students with disabilities to improve their physical and mental health levels. Sports Science Research, (1), 27-29.
- Guo, M. G., Wu, X., & Chen, J. (2007). Research on the psychological health of people with disabilities and its relationship with physical exercise. Journal of Beijing Sport University, (2), 189-191.
- Zhang, L. W., & Mao, Z. X. (1995). The relationship between physical exercise and psychological health (review). Journal of Guangzhou Sport University, (4), 41-43.
- Zhang, F. X., & Wang, G. (2002). On the purpose, significance, and characteristics of sports activities for people with disabilities. Physical Education and Research, (1), 11-19.
- Miao, Y. Y. (2011). An experimental study on the impact of sports game activities on promoting the physical fitness of young children. Beijing: Capital University of Physical Education and Sports.
- Wu, X. L. (2003). The role of sports games in the quality education of young children. Journal of Physical Education, (4), 111-113.
- Yu, J. (1997). On the value of sports games in early childhood education. Shandong Sports Science and Technology, (3), 66-67.
- Wang, J. N., & Lan, J. J. (2011). A survey study on the psychological health and level of physical exercise of deaf students. Chinese Journal of Health Psychology, (11), 1360-1361.
- Zhang, J. (2002). A survey study on the impact of sports games on the physical and mental health development of young children. Hubei Sports Science and Technology, (3), 103-107.
- Yang, S. H. (2001). Analysis of SCL-90 evaluation results for students with disabilities in special education colleges. Chinese Journal of Special Education, (2), 27-32.
